In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transferred or converted from one form to another. This is a fundamental principle of thermodynamics and classical mechanics. The total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant over time.
Energy may flow into or out of the system, but the sum of all forms of energy in the system remains constant.
The answer to this question is both yes and no. Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be converted from one form to another. For example, when a car burns gasoline, the chemical energy in the gas is converted into heat and kinetic energy, which powers the car.
Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed, But It Can Be Converted From One Form to Another
In the physical sciences, energy is the capacity of a system to do work. Energy exists in several forms, such as electromagnetic radiation, gravitational potential] electrical potential, sound, and thermal energy. These can be categorized into two main types: kinetic energy, which depends on motion, and potential energy, which depends on a position relative to other objects.
Chemical energy is associated with the rearrangement or reorganization of atoms and molecules during chemical reactions. Nuclear energy is released during nuclear fission or nuclear fusion reactions. Other forms include radiant energy, elastic energy, magnetic energy,[and gravitational energy.
The SI unit of energy is the joule (J), defined as the work done by a force of one newton when its point of application moves one meter in the direction of that force.[19] Total energy values depend only on a system’s state; they are independent of any observer’s frame of reference.
In classical mechanics, Newton’s laws of motion imply energy conservation. “Energy” can also be used informally to refer to an individual’s (or society’s) ability to choose how resources are used. It also refers to the fuel consumed by equipment (such as an automobile engine) and/or produced by that equipment (such as gasoline).
For Example, Energy Can Be Converted From Chemical Energy to Heat Energy
In physics, energy is the property that must be transferred to an object to perform work on, or to heat, the object. – Energy can be converted from one form to another. -For example, chemical energy can be converted to heat or electrical energy.
The energy conservation law states that the total energy in a closed system remains constant; it cannot be created or destroyed.
Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed, But It Can Be Converted From One Form to Another
Thi.s is one of the most basic laws of physics, and it’s something that we see happening all around us all the time. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed – but it can be converted from one form to another. We see this happening with light all the time.
When sunlight hits a glass, some energy is converted into heat energy, which makes the glass warm to the touch. Similarly, when we burn wood in a fire, the chemical energy in the wood is converted into heat and light energy. But it’s not just light that obeys this law – all forms of energy follow it. Let’s look at some examples:
Example One
when you do work – like lifting a heavy object – you’re converting your body’s chemical energy into kinetic energy (energy of motion). And when a car brakes, its kinetic energy is converted into heat energy. The law also applies to matter: Matter cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another.
Example Two
When water evaporates (turns from liquid to gas), the atoms don’t change – they move further apart. Likewise, when milk goes off and turns into cheese and yoghurt, again, no new atoms are being created – they’re just rearranging themselves into different molecules. This law is incredibly important in many areas of science.
In particular, it helps us understand how stars work: They convert hydrogen atoms into helium atoms through nuclear fusion reactions (a process that requires additional energy input). This conversion releases huge amounts of heat and light energy, which powers the star for billions of years!
Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed Which Law?
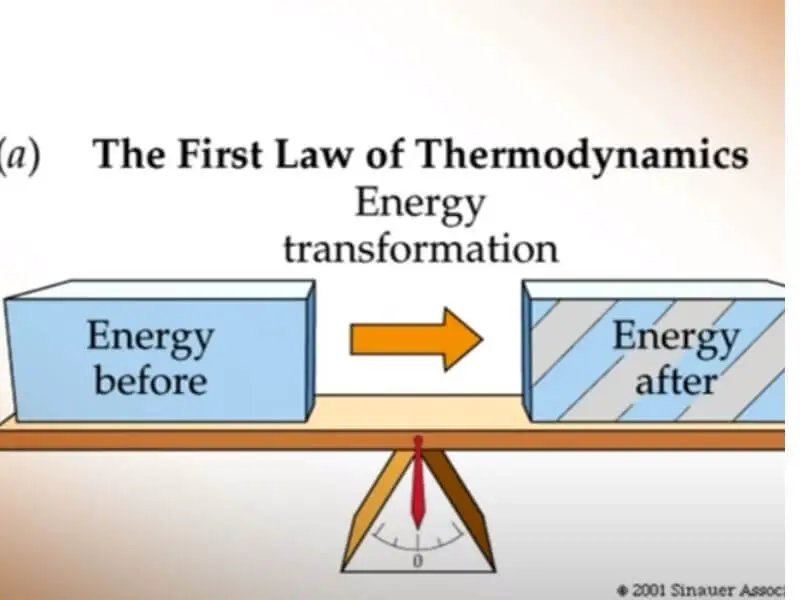
The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in the universe is always constant. The law is one of the most important principles in physics and has far-reaching applications in many different fields.
In very simple terms, the law of energy conservation says that you can’t get something for anything. It’s a basic principle that governs all physical systems, from subatomic particles to entire galaxies. For something to happen, there must be a corresponding change in energy somewhere else.
This principle was first proposed by German physicist Hermann von Helmholtz in 1847, though it wasn’t fully understood until the late 19th century. Since then, it has been confirmed over and over again through countless experiments and observations. It’s now considered one of the most well-established laws in all physics.
The law of conservation of energy has some important consequences:
- One is that it implies the existence of an ultimate energy source: whatever created the universe must have supplied all its initial energy (and still supplies any additional needed energy).
- Another consequence is that it limits how much efficiency we can ever hope to achieve in converting one type of energy into another; no process can be 100% efficient because some energy must always be lost as heat or other forms of pollution.
If Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed, Where Did It Come From?
In the mid-nineteenth century, British physicist James Joule conducted a series of experiments to discover the relationship between heat and mechanical work. One of his most famous experiments involved attaching a weight to a string wrapped around a pulley. As the weight fell, it turned the pulley, which rotated a paddle wheel in a bucket of water.
The experiment showed that heat is always generated when mechanical work is done on an object. Joule’s work led to the development of the energy conservation law, which states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed—it can only be transformed from one form to another. This law is one of the most important laws in physics and has far-reaching implications.
It means that the total amount of energy in the universe is constant; it also means that if we want to generate energy (for example, by burning fossil fuels), we must first extract it from somewhere else—from the Sun or radioactive decay deep within Earth’s crust.
The energy conservation law also has important implications for understanding how the universe began. If energy cannot be created or destroyed, then it must have always existed—which means that there must have been an infinite amount of time for everything that we see today (including ourselves) to come into existence through a process of transformation from other forms of energy.
Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed Einstein
In his famous equation, E=mc2, Albert Einstein showed that energy and mass are equivalent. This means that energy can neither be created nor destroyed—it can only be transformed from one form to another. The total energy in the universe is constant, even as it changes forms.
For example, when coal is burned to produce heat or electricity, the mass of the coal is converted into energy. But the total amount of matter and energy remains the same—what was once part of the coal is now part of the heat or light produced. Similarly, massive amounts of energy are released when a nuclear bomb explodes, but no new matter is created.
The atoms that were split apart simply release their stored energy.
If Energy Cannot Be Created, How is the Universe Expanding?
The universe is expanding because energy is being created. The amount of energy in the universe is constantly increasing, and as a result, the universe is getting bigger. But where does this extra energy come from?
Some scientists believe that it comes from the vacuum of space itself. According to this theory, the vacuum is not really empty; it contains a tiny amount of energy that can be converted into matter and radiation. Over time, this process could account for all the extra energy in the universe, making it possible for the universe to keep expanding indefinitely.
Other scientists believe that the extra energy in the universe comes from so-called dark energy. This invisible form of energy fills all of space and drives the universe’s expansion. Dark energy is still very mysterious, but scientists think it may be responsible for most of the acceleration of cosmic expansion.
Can Energy Be Created?
The short answer is yes; energy can be created. Energy is the ability to do work, and it comes in many forms, including electrical, thermal, nuclear, chemical, and gravitational potential energy. Energy can be converted from one form to another or transferred from one object to another.
It cannot be destroyed because:
- The first law of thermodynamics states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed—it can only change its form or transfer from one place to another.
- The second law of thermodynamics says that when energy changes form or transfers, some of it is always lost as heat or friction.
So if we want to create usable energy, we have to start with a larger amount of unusable energy (like heat from the sun or nuclear radiation). Then we have to use technology to convert it into a useful form like electricity. Even then, there will always be some loss along the way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Is the Principle of Energy Conservation?
The principle of energy conservation, also known as the First Law of Thermodynamics, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transferred or changed from one form to another. For instance, kinetic energy can be converted into potential energy and vice versa, but the total energy within a closed system remains constant.
Is It True or False That Energy Cannot Be Created or Destroyed?
It is true that energy cannot be created or destroyed, according to the Law of Conservation of Energy. This law underlies all physical phenomena and is a fundamental principle of our understanding of physics.
What Does It Mean When We Say Energy Cannot Be Destroyed?
When we say that energy cannot be destroyed, it means that energy can never vanish or disappear. It can only be transferred or transformed into other forms. For instance, in a light bulb, electrical energy is transformed into light and heat energy. The total energy before and after the transformation remains the same.
Can Energy Be Created From Nothing?
No, energy cannot be created from nothing according to our current understanding of physics and the Law of Conservation of Energy. The energy present in a system must have been transferred from elsewhere and cannot simply appear out of nowhere.
Are There Any Exceptions to the Law of Conservation of Energy?
As of my last update in September 2021, there were no known exceptions to the Law of Conservation of Energy in classical physics. However, in the quantum realm, there are certain phenomena like quantum fluctuations that appear to momentarily create particles (and thus energy) out of ‘nothing’, but these still respect a generalized version of energy conservation known as the conservation of four-momentum. In general, the Law of Conservation of Energy holds true for all processes and events we observe in the universe.
Conclusion
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, true or false. This is a common question with a simple answer. The law of energy conservation states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be converted from one form to another.
In other words, the total amount of energy in the universe is always the same.
Relevant Resources:
