As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, finding sustainable solutions for everyday needs has become more critical than ever. One of the most significant contributors to carbon emissions is the energy used to heat and cool buildings. In this regard, finding ways to reduce energy consumption and transition to sustainable energy sources has become a top priority. Ground-source heat pumps have emerged as one of the most efficient and environmentally friendly options available today.

Ground-source heat pumps are a relatively new technology that uses the constant temperature of the earth to regulate indoor temperatures. Compared to traditional heating and cooling systems that rely on burning fuel or using electricity, ground-source heat pumps use the earth’s natural energy to provide heating and cooling. They work by transferring heat energy between the earth and a building, either to heat or cool the interior space as needed. This technology is gaining momentum as people seek out energy-efficient and sustainable solutions to their heating and cooling needs.
How Ground-Source Heat Pumps Work?
Ground-source heat pumps work by utilizing the earth’s natural energy to heat or cool a building. The system consists of a series of pipes, known as a loop, that is buried underground. These pipes are filled with a heat transfer fluid, usually a mixture of water and antifreeze, that circulates through the loop.
In the winter, the fluid absorbs heat from the ground and carries it back to the heat pump, which compresses it to increase the temperature further. The heat pump then uses the heated fluid to warm the air inside the building. In the summer, the process is reversed, and the heat pump uses the loop to transfer heat from the building into the ground, effectively cooling the interior space.
The heat transfer fluid in the loop can be circulated in two ways: through a closed-loop or an open-loop system. Closed-loop systems are the most common and involve a continuous circulation of fluid through the loop. The fluid absorbs heat from the ground and carries it to the heat pump, where it’s used to heat the building. The cooled fluid is then sent back to the loop to start the process again.
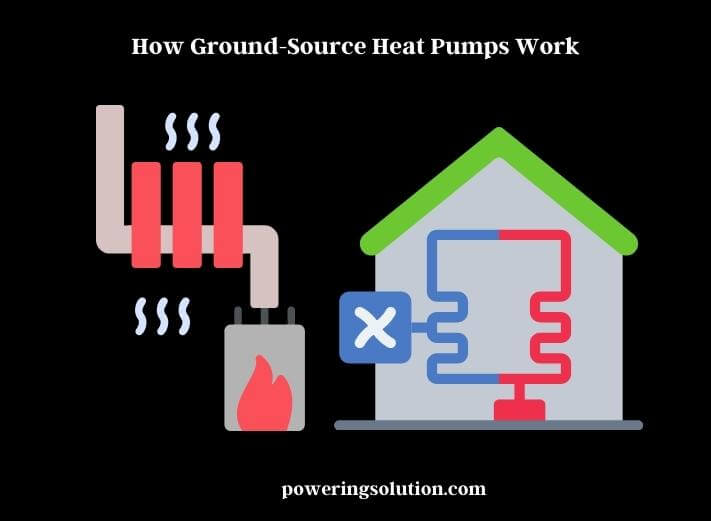
Open-loop systems, on the other hand, use groundwater as the heat source. Water is pumped from a well or other source and circulated through the heat pump. As the water passes through the heat exchanger, it absorbs heat from the earth and is then discharged back into the ground.
Ground-source heat pumps are incredibly efficient and can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. They are also environmentally friendly, as they rely on the earth’s natural energy rather than burning fossil fuels.
Types of Ground-Source Heat Pumps
There are two main types of ground-source heat pumps: closed-loop systems and open-loop systems. Let’s take a closer look at each of these types.
Closed-loop systems are the most common type of ground-source heat pump. They are typically installed in a horizontal or vertical configuration. In a horizontal configuration, pipes are laid in trenches that are dug in the ground, while in a vertical configuration, pipes are drilled into boreholes that are several hundred feet deep. The heat transfer fluid flows through these pipes, absorbing heat from the ground and transferring it to the heat pump, where it’s used to heat or cool the building. Closed-loop systems are ideal for most residential and commercial applications and can be used in a variety of soil conditions.
Open-loop systems, on the other hand, use groundwater as a heat source. They are typically more efficient than closed-loop systems, but they require access to a sufficient supply of high-quality groundwater. Open-loop systems draw water from a well or other source, circulate it through the heat pump, and then discharge it back into the ground. They are best suited for buildings that require high heating and cooling loads, such as large commercial buildings or industrial facilities.

Another type of ground-source heat pump is the hybrid system, which combines a ground-source heat pump with a traditional heating and cooling system. In this system, the ground-source heat pump is used as the primary heating and cooling system, with the traditional system serving as a backup during peak demand or extreme weather conditions.
Regardless of the type of ground-source heat pump, the technology offers a sustainable solution for heating and cooling buildings, reducing energy consumption, and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
Advantages of Ground-Source Heat Pumps
Ground-source heat pumps offer several advantages over traditional heating and cooling systems. Let’s take a look at some of the most significant benefits of this technology:
- Energy efficiency: Ground-source heat pumps are incredibly efficient, typically using 25-50% less energy than traditional heating and cooling systems. This efficiency translates into lower energy bills and reduced carbon emissions.
- Long lifespan: Ground-source heat pumps typically have a lifespan of 25 years or more, making them a durable and long-lasting solution for heating and cooling buildings.
- Low maintenance: Ground-source heat pumps require very little maintenance, as they have fewer moving parts than traditional systems. This reduces the need for expensive repairs and helps to extend the system’s lifespan.
- Quiet operation: Ground-source heat pumps operate quietly, making them an excellent choice for residential buildings where noise can be a concern.
- Versatility: Ground-source heat pumps can be used for both heating and cooling, making them a versatile solution for any building.
- Sustainable: Ground-source heat pumps rely on the earth’s natural energy, making them a sustainable and environmentally friendly option for heating and cooling buildings.
- Government incentives: Many governments offer incentives and rebates for the installation of ground-source heat pumps, making them a cost-effective option for many building owners.
Installation of Ground-Source Heat Pumps
The installation of ground-source heat pumps typically involves several steps, including site analysis, system design, and actual installation. Here’s a closer look at each of these steps:

| Site analysis | Before installing a ground-source heat pump, a thorough site analysis is necessary to determine if the site is suitable for a ground-source heat pump system. Factors such as soil type, water availability, and land size will be considered during this process. |
| System design | Once the site analysis is complete, a system design is created. This design will take into account the size and layout of the building, as well as the heating and cooling requirements. The design will also specify the type of ground-source heat pump system to be installed. |
| Installation | The actual installation of the ground-source heat pump system involves drilling or digging trenches for the installation of the piping. The piping is typically buried several feet below the surface to take advantage of the earth’s natural temperature. Once the piping is installed, the heat pump unit is installed inside the building. |
| Testing and commissioning | After installation, the ground-source heat pump system will be tested and commissioned to ensure that it’s working correctly. This includes checking the flow rate of the heat transfer fluid, as well as testing the heat pump unit itself. |
| Maintenance | Like any heating and cooling system, ground-source heat pumps require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This includes checking the flow rate of the heat transfer fluid, changing filters, and inspecting the heat pump unit. |
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Like any heating and cooling system, ground-source heat pumps require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Here are some of the maintenance tasks and troubleshooting steps that may be necessary for a ground-source heat pump system:
- Regular maintenance: Regular maintenance of a ground-source heat pump system includes tasks such as checking the flow rate of the heat transfer fluid, cleaning or replacing air filters, and inspecting the heat pump unit. It’s also important to have the system inspected and serviced by a professional at least once a year to ensure that it’s working correctly.
- Troubleshooting: If your ground-source heat pump system is not working correctly, there are several troubleshooting steps you can take. For example, if the system is not heating or cooling effect, check the air filters and make sure they’re clean. If the problem persists, contact a professional to inspect the system.
- Refrigerant leaks: Refrigerant leaks can occur in ground-source heat pumps, just like any other type of HVAC system. If you suspect a refrigerant leak, contact a professional immediately, as these leaks can be dangerous and require specialized equipment to repair.
- Electrical issues: Ground-source heat pumps rely on electrical components to function correctly. If you notice electrical issues such as tripped breakers or blown fuses, contact a professional to diagnose and repair the problem.
- Water leaks: Water leaks can occur in the piping system of a ground-source heat pump, particularly if the piping is not installed correctly or becomes damaged. If you notice water leaks around the heat pump unit or in the piping system, contact a professional to diagnose and repair the problem.
If you perform regular maintenance and address any issues promptly, you can ensure that your ground-source heat pump system operates efficiently and effectively for many years to come. If you’re unsure about how to maintain or troubleshoot your system, contact a professional for assistance.
Comparing Ground-Source Heat Pumps to Other Heating and Cooling Systems
Ground-source heat pumps offer several advantages over other types of heating and cooling systems.
Efficiency
Ground-source heat pumps are highly efficient, using the earth’s natural temperature to heat and cool a building. In contrast, traditional HVAC systems rely on fossil fuels or electricity to generate heat and cool air, which can be less efficient and more expensive.
Environmental Impact
Ground-source heat pumps are a sustainable and environmentally friendly heating and cooling solution, producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions than traditional HVAC systems. They also have a smaller carbon footprint than other renewable energy systems, such as solar or wind power.
Cost
While the upfront cost of a ground-source heat pump system is higher than traditional HVAC systems, it can provide significant long-term cost savings due to its high efficiency and lower operating costs.
Maintenance
Ground-source heat pumps require less maintenance than traditional HVAC systems, as there are fewer moving parts and the system is less prone to wear and tear.
Noise
Ground-source heat pumps are typically quieter than traditional HVAC systems, as the heat pump unit is located indoors and there is no need for an outdoor compressor unit.
Climate Suitability
Ground-source heat pumps are suitable for a wide range of climates, as they can extract heat from the earth even in colder temperatures. In contrast, traditional HVAC systems may struggle to provide efficient heating in very cold climates.
Ground-source heat pumps offer a highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective solution for heating and cooling a building. While they may have a higher upfront cost, their long-term cost savings, environmental benefits, and ease of maintenance make them an attractive option for many homeowners and businesses.
Applications for Ground-Source Heat Pumps
Ground-source heat pumps are a versatile and sustainable solution for both residential and commercial applications.
Ground-source heat pumps can be installed in homes to provide efficient heating and cooling. They can be used with radiant floor heating, forced air heating, or a combination of both.
Ground-source heat pumps are also suitable for commercial applications, such as schools, hospitals, and office buildings. They can provide efficient heating and cooling for large spaces, reducing energy costs and carbon emissions.
Ground-source heat pumps can be used to heat water for domestic or commercial use. They can be integrated with existing hot water systems or used as a standalone system.
Ground-source heat pumps are an essential component of geothermal heating and cooling systems. These systems use the constant temperature of the ground to provide heating and cooling for homes and buildings.
Ground-source heat pumps can be used to heat swimming pools, providing a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional pool heaters.
Ground-source heat pumps can be used for agricultural applications, such as heating greenhouses or providing heating and cooling for livestock buildings.
Financial Incentives and Cost Savings
One of the biggest advantages of ground-source heat pumps is their potential for cost savings and financial incentives.
Ground-source heat pumps are more efficient than traditional heating and cooling systems, which means they use less energy to provide the same level of comfort. This translates into lower energy bills over time.
Ground-source heat pumps have fewer moving parts than traditional heating and cooling systems, which means they require less maintenance and have lower repair costs.
Ground-source heat pumps have a longer lifespan than traditional heating and cooling systems, which means you’ll save money in the long run by avoiding the need for replacement.
There are often financial incentives available to homeowners and businesses that install ground-source heat pumps. These can include tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives that can significantly offset the upfront cost of installation.
Installing a ground-source heat pump can increase the value of your property, which can be beneficial if you plan to sell your home or business in the future.
It’s important to note that while ground-source heat pumps may have higher upfront costs than traditional heating and cooling systems, the long-term cost savings can outweigh the initial investment. Financial incentives can make installation more affordable for homeowners and businesses.
Future of Ground-Source Heat Pumps
The future of ground-source heat pumps is looking bright as more and more people become aware of their benefits.
Manufacturers are constantly working on improving the efficiency of ground-source heat pumps. This could lead to even greater energy savings and lower operating costs in the future.
As with other home appliances, ground-source heat pumps are likely to become more integrated with smart home technology in the future. This could include features such as remote control and monitoring, and the ability to adjust settings based on usage patterns.
As the popularity of ground-source heat pumps grows, installation processes are likely to become more streamlined and efficient. This could reduce installation costs and make it easier for homeowners and businesses to adopt this technology.
As renewable energy becomes more mainstream, it’s likely that more people will choose ground-source heat pumps as a sustainable heating and cooling solution. This increased adoption could lead to more research and development in the field, further improving the technology.
Ground-source heat pumps can be integrated with other renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to provide even greater energy savings and reduce reliance on non-renewable energy sources.
If you want to know can I replace a solar rechargeable battery with a regular battery? Click the article to know the answer.
Last Remarks
Ground-source heat pumps offer a sustainable solution for heating and cooling that can benefit both homeowners and businesses. They are energy-efficient, have lower maintenance costs, and have a longer lifespan than traditional heating and cooling systems. Financial incentives and increased property value make ground-source heat pumps a cost-effective choice.
Looking to the future, ground-source heat pumps are likely to continue to evolve and improve in terms of efficiency, smart technology integration, and adoption. As renewable energy becomes more mainstream, it’s likely that ground-source heat pumps will become an even more popular choice for sustainable heating and cooling solutions.
Ground-source heat pumps offer a range of benefits that make them a strong choice for anyone looking to reduce their environmental impact and save money on heating and cooling costs. With their potential for energy savings, long lifespan, and financial incentives, ground-source heat pumps are a sustainable solution that can help create a more sustainable future for us all.
