Batteries are devices that store energy and release it in an electric current. The word “battery” comes from the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta, who invented the first battery in 1800. A typical battery has two electrically connected metal plates—the cathode (positive end) and the anode (negative end).
When the battery is not in use, electrons build up on the cathode. When you connect a load (such as a light bulb) to the battery, electrons flow through the load from the cathode to the anode, producing an electric current.
Batteries are one of the most essential inventions in our modern world. They power everything from our cell phones to our cars. But how do batteries work?
Batteries are essentially made up of two different types of metal, which are separated by a liquid or gel. When the battery is charged, the positively charged metal ions flow to the negative electrode and vice versa. This creates an electrical potential difference between the two electrodes, which is what powers our devices.
The chemical reaction that occurs inside a battery is known as an electrochemical reaction. This reaction is responsible for producing the electrical energy that powers our devices.
There are many different types of batteries, but they all work using these basic principles of chemistry.
So next time you reach for your phone or hop in your car, remember that it’s all thanks to chemistry!
How Does Battery Chemistry Work?
Batteries are devices that store and release electrical energy. They have two terminals, called the anode and the cathode. The anode is where electrons flow into the battery, and the cathode is where they flow out.
In between these two terminals is a chemical reaction that generates electricity. This reaction involves moving ions from one place to another. Ions are atoms that have lost or gained electrons, making them electrically charged.
The anode is usually made of a metal like lithium or lead, while the cathode is typically made of a material like carbon. When the battery is not in use, these two materials are separated by an electrolyte—a substance that ions can travel through.
When you connect a battery to a circuit, electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through this electrolyte.
This sets off a chain reaction in which ions flow back and forth between the electrodes, generating electricity in the process.
Do Batteries Use Chemistry?
Batteries use a chemical reaction to create an electric current. The most common type of battery is the lead acid battery, which uses a chemical reaction between lead and sulfuric acid to create an electric current.
What is the Chemical Reaction in a Battery Called?
In a battery, there are two chemical reactions occurring simultaneously. The first reaction is known as oxidation and it occurs at the anode. This reaction causes electrons to be released from the anode into the external circuit.
The second reaction is called reduction and it occurs at the cathode. In this reaction, electrons are taken in by the cathode from the external circuit. These two reactions work together to create an electric current that can be used to power electrical devices.
How Do Batteries Work for Kids?
How Do Batteries Work for Kids? Batteries are a common power source for many devices, including toys, flashlights, and remote control cars. But how do they work?
Read on to find out! A battery is made up of one or more cells. Each cell has two electrodes, one positive and one negative.
The electrodes are separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is connected to a circuit, electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through the electrolyte. This flow of electrons creates an electric current that powers the device.
The strength of the current produced by a battery depends on the number of cells it has. A single-cell battery produces a small current, while a multi-cell battery produces a larger current. The size of the battery also affects its strength—a AA battery produces more power than a AAA battery.
How Do Batteries Work Simple Explanation?
Batteries are a common power source in many electronic devices. But how do they work? This post will explain the basics of how batteries work, in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
Batteries have two terminals, positive and negative. Inside the battery, there are chemical reactions that generate electrons. The negative terminal is where these electrons collect.
When you connect a device to the battery using wires, the electrons flow from the negative terminal through the wires to the positive terminal. This flow of electrons provides power to your device. The chemical reactions inside a battery will eventually cause it to run out of power and need to be replaced.
How to Make a Battery Chemistry?
Are you interested in learning how to make battery chemistry? Batteries are essential for many of our electronic devices, so it’s no wonder that there is a lot of interest in them. Battery chemistries can be complex, but with a little bit of knowledge and some basic materials, you can make your own battery at home.
The first step is to gather the necessary materials. For this project, you will need:
- One cup of white vinegar;
- One cup of water;
- One tablespoon of salt;
- A clean glass jar with a lid;
- A strip of copper wire.
How Do Batteries Store Energy?
Batteries store energy in a chemical form that can be released on demand to power electrical devices. The three most common types of batteries are lead-acid, nickel-cadmium, and lithium-ion. Each type of battery has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Lead-acid batteries are the least expensive and have the longest life span, but they are also the heaviest and require regular maintenance. Nickel-cadmium batteries are more expensive than lead-acid batteries, but they are lighter and don’t require as much maintenance. Lithium-ion batteries are the most expensive, but they are also the lightest and have the longest life span.
Is Chemical Energy the Main Source of Energy Storage in Batteries?
Chemical energy in battery technology is indeed the main source of energy storage. Batteries function by converting chemical energy into electrical energy through a series of reactions. When a battery is charged, chemical reactions store energy in the form of electrochemical potential, which is then released as electrical energy when the battery is discharged. This efficient energy storage mechanism allows batteries to power a wide range of devices and applications.
How Does a Battery Work in a Circuit?
A battery is a device that stores energy and converts it into electrical current. It consists of one or more cells, each of which contains a positive and negative electrode separated by an electrolyte. When the battery is connected to a circuit, the chemical reaction between the electrodes and electrolyte produces an electrical current that flows through the circuit.
The amount of electrical current produced by a battery depends on its size and type. The larger the battery, the more electrons it can store and release, and thus the greater the amount of current it can produce. The type of battery also affects its output; for example, a lead-acid battery produces more current than a nickel-cadmium battery of the same size.
Batteries are classified according to their chemistry; common types include lead-acid, nickel-cadmium (NiCd), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), and alkaline. Each type has advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, weight, discharge time, capacity, voltage, self-discharge rate, environmental impact, safety, and other factors.
:Can White Vinegar Help Prevent Battery Damage and Extend Battery Life?
White vinegar is a versatile household item known for its ability to neutralize battery acid. By neutralizing battery acid with vinegar, you can prevent damage and extend the life of your batteries. This simple and cost-effective method can help protect your electronic devices from corrosion and ensure they stay powered for longer.
Do Batteries Make Electricity?
Batteries are one of the most essential components in making electricity. While many people think that batteries simply store power, they actually play a far more important role in the process. In order for a battery to work, it must be able to create and maintain an electric current.
This is done by using a chemical reaction to convert stored energy into electrical energy. The first battery was invented in 1799 by Italian physicist Alessandro Volta, and it has been used in a variety of applications ever since. Batteries come in all shapes and sizes, from small button batteries to large car batteries.
They can be made from a variety of materials, but most contain some form of acid or metal oxide. The chemical reaction that takes place inside a battery produces electrons, which flow through an external circuit and power whatever device is attached to it. Batteries are often used in devices that require a constant supply of electricity, such as clocks or smoke detectors.
They are also commonly used in portable electronic devices like laptops and cell phones. Many automobiles also rely on batteries to start the engine and provide power for accessories like lights and radios.
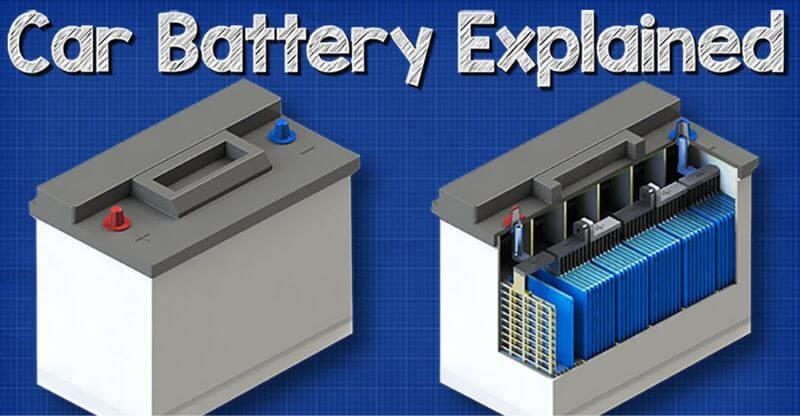
How Do Rechargeable Batteries Work?
Batteries are a common power source for many devices we use daily. Most batteries are disposable, meaning they cannot be recharged and must be replaced once they run out of power. However, rechargeable batteries can be used multiple times before needing to be replaced.
So, how do rechargeable batteries work? Rechargeable batteries store energy in chemical form, much like disposable batteries. When a device is connected to a power source, the battery charges, and the chemicals inside the battery react to create an electric current.
This current then powers the device. Once the device is disconnected from the power source, the battery discharges, and the chemicals inside revert back to their original state. The battery can now be recharged and used again.
There are several types of rechargeable batteries available on the market today, including lithium-ion, nickel-cadmium (NiCd), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), lead acid, and others. Each type of battery has its own benefits and drawbacks in terms of cost, capacity, weight, discharge rate, self-discharge rate, memory effect, and more. Choosing the right type of rechargeable battery for your needs is important to get optimal performance out of it.
You have to know that Nuclear kinetic energy is the energy of motion of particles in an atom.
Wrap Up
Batteries are devices that store electrical energy and convert it into chemical energy. The most common type of battery is the lead-acid battery, which uses a lead anode and a sulfuric acid cathode. When the lead anode and sulfuric acid cathode are connected by an electrolyte, a chemical reaction takes place that produces electrical energy.
Other types of batteries include lithium-ion batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries, and nickel-metal hydride batteries. Each type of battery has its own advantages and disadvantages. Lead-acid batteries are the most economical but have a shorter lifespan than other types of batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries are more expensive but can be recharged many times before they need to be replaced. Nickel-cadmium batteries are less expensive than lithium-ion batteries but must be disposed of properly because they contain toxic materials. Nickel-metal hydride batteries are similar to lithium-ion batteries but use hydrogen instead of carbon in their electrodes.
