Solar panels are becoming increasingly popular as an alternative energy source, thanks to their numerous advantages such as low environmental impact, long lifespan, and reduced energy costs. With the number of solar panel types available in the market, choosing the right one for your specific needs can be a daunting task.

This article aims to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the different types of solar panels, their advantages, and disadvantages, as well as their suitability for different environments and applications.
By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of which type of solar panel is best suited for your needs, making it easier for you to make an informed decision. So, let’s dive into the world of solar panels and explore the various types available in the market.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are one of the most widely used types of solar panels for residential and commercial applications. They are made from a single silicon crystal, which gives them a uniform, dark color and a high level of efficiency. In fact, monocrystalline solar panels are currently the most efficient type of solar panel on the market, with an efficiency rate of up to 22%.
The manufacturing process for monocrystalline solar panels is complex and requires a high degree of precision. It involves growing a single crystal of silicon in a controlled environment, then cutting it into thin wafers that are used to make individual solar cells. The resulting solar panels are highly durable and long-lasting, with a typical lifespan of 25-30 years.
One of the main advantages of monocrystalline solar panels is their high efficiency. Because they are made from a single, uniform crystal, they are able to convert a greater amount of sunlight into electricity than other types of solar panels. This means that you can generate more power from a smaller number of panels, which can be especially beneficial for residential applications where space may be limited.
Another advantage of monocrystalline solar panels is their sleek and uniform appearance. The dark color and smooth texture of the panels can blend in well with a variety of roofing materials, making them a popular choice for homeowners who want a more streamlined look for their solar panel installation.
While monocrystalline solar panels are generally more expensive than other types of solar panels, their high efficiency and long lifespan can make them a good investment in the long run. Many manufacturers offer warranties and guarantees on their monocrystalline solar panels to ensure their quality and performance over time.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels are another popular type of solar panel that is commonly used in residential and commercial applications. Unlike monocrystalline solar panels, which are made from a single crystal of silicon, polycrystalline solar panels are made from multiple smaller crystals of silicon that are melted together to form a single wafer.
The manufacturing process for polycrystalline solar panels is simpler and more cost-effective than the process for monocrystalline solar panels. This makes them a more affordable option for those who want to invest in solar energy without breaking the bank. However, polycrystalline solar panels are slightly less efficient than monocrystalline solar panels, with an efficiency rate of up to 20%.
Despite their slightly lower efficiency, polycrystalline solar panels still offer a range of benefits for homeowners and businesses looking to generate clean, renewable energy. One of the main advantages of polycrystalline solar panels is their affordability. Because the manufacturing process is simpler and less costly, polycrystalline solar panels are typically more budget-friendly than other types of solar panels.
Another advantage of polycrystalline solar panels is their durability. Like monocrystalline solar panels, polycrystalline solar panels are designed to withstand the elements and last for many years. They can be a good investment for homeowners and businesses that want to generate their own energy and reduce their carbon footprint over time.
The decision to choose polycrystalline solar panels over other types of solar panels depends on a variety of factors, including budget, space constraints, and energy needs. While they may not be the most efficient type of solar panel on the market, they are a cost-effective and durable option for those who want to invest in solar energy.
Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are a type of solar panel that is made by depositing thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate, such as glass, metal, or plastic. They are also known as amorphous or flexible solar panels, due to their flexibility and ability to be installed on curved surfaces.
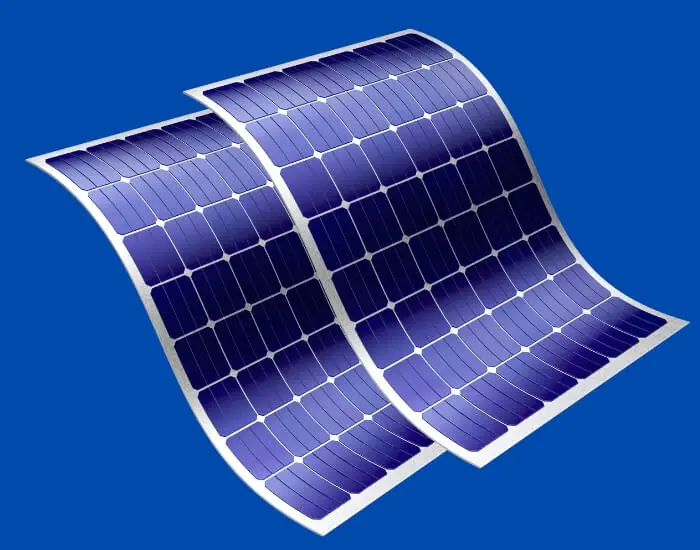
Advantages of Thin-Film Solar Panels
One of the biggest advantages of thin-film solar panels is their flexibility and versatility in installation. They are lightweight and can be installed on a range of surfaces, including curved and irregular surfaces, making them a popular option for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). They have a lower carbon footprint than other solar panel types, as they require less energy to manufacture. Thin-film solar panels are also less affected by high temperatures, which can cause a decrease in efficiency in other solar panel types.
Disadvantages of Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels have a lower efficiency rate than other types of solar panels, meaning that they require more surface area to produce the same amount of electricity. This makes them a less suitable option for areas with limited space for solar panel installation. They have a shorter lifespan compared to other solar panel types, with an average warranty period of 5-10 years.
Applications and Suitability for Different Climates and Environments
Thin-film solar panels are a good option for areas with high temperatures or fluctuating weather conditions, as they are less affected by temperature changes compared to other solar panel types. They are also suitable for curved and irregular surfaces, making them a popular option for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV). They may not be the best option for areas with limited space for solar panel installation, as their lower efficiency rate may result in a lower output of electricity.
Cost Analysis and Average Lifespan of Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are generally less expensive than other types of solar panels, due to their simpler manufacturing process. On average, they cost around 10-20% less than their crystalline counterparts. However, their shorter lifespan may result in higher replacement costs in the long run. On average, thin-film solar panels have a lifespan of 5-10 years.
Examples of Popular Thin-Film Solar Panel Manufacturers
Some of the most popular thin-film solar panel manufacturers include First Solar, SunPower, and Solar Frontier. These companies offer a range of thin-film solar panels with varying levels of efficiency and warranty periods.
Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels are a type of solar panel that can capture sunlight from both sides of the panel, increasing their energy production efficiency. They are also known as double-sided solar panels.

How Bifacial Solar Panels Work?
Bifacial solar panels work by capturing light from both sides of the panel. They have a transparent backing material, which allows sunlight to pass through and be reflected onto the backside of the panel. This increases the amount of energy produced by the panel. Bifacial solar panels can be installed in a variety of configurations, including ground-mounted, rooftop, and vertical installations.
Advantages of Bifacial Solar Panels
One of the biggest advantages of bifacial solar panels is their increased energy production efficiency. Capturing sunlight from both sides of the panel, they can produce up to 27% more energy compared to traditional, single-sided solar panels. Bifacial solar panels are also more resistant to soiling and shading, as they can still produce energy from the backside of the panel even if the front is partially covered. Additionally, they have a longer lifespan compared to other solar panel types, with an average warranty period of 25 years.
Disadvantages of Bifacial Solar Panels
One of the main disadvantages of bifacial solar panels is their higher cost compared to traditional, single-sided solar panels. They also require more planning and expertise during installation, as their effectiveness is highly dependent on factors such as location, shading, and angle of installation. Additionally, bifacial solar panels may not be suitable for areas with high wind or extreme weather conditions, as their two-sided design may make them more vulnerable to damage.
Applications and Suitability for Different Climates and Environments
Bifacial solar panels are a good option for areas with high levels of reflected sunlight, such as snow-covered surfaces or highly reflective rooftops. They are also a good option for areas with limited space for solar panel installation, as their increased energy production efficiency means that fewer panels are needed to produce the same amount of electricity. However, they may not be the best option for areas with high winds or extreme weather conditions, as their two-sided design may make them more vulnerable to damage.
Cost Analysis and Average Lifespan of Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels are generally more expensive than traditional, single-sided solar panels, due to their increased energy production efficiency and more complex design. On average, they cost around 10-30% more than traditional solar panels. However, their longer lifespan and increased energy production efficiency may result in cost savings in the long run. On average, bifacial solar panels have a lifespan of 25 years.
Examples of Popular Bifacial Solar Panel Manufacturers
Some of the most popular bifacial solar panel manufacturers include LG, Sunpreme, and Trina Solar. These companies offer a range of bifacial solar panels with varying levels of efficiency and warranty periods.
Other Types of Solar Panels
Aside from the four main types of solar panels – monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film, and bifacial – there are also other types of solar panels that are gaining popularity in the industry.
Concentrated Solar Panels (CSP)
Concentrated solar panels, also known as concentrated solar power or CSP, use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, which heats up a fluid or gas that is used to generate electricity. CSP systems are typically larger and more complex than traditional solar panels, and they require direct sunlight to function effectively. They can generate electricity even after sunset, thanks to their ability to store heat energy in insulated tanks.
Hybrid Solar Panels
Hybrid solar panels are a combination of two or more types of solar panel technologies, such as crystalline silicon and thin film. They are designed to take advantage of the strengths of each technology while mitigating their weaknesses. For example, hybrid solar panels may combine the efficiency of monocrystalline solar panels with the affordability of polycrystalline panels.
Organic Solar Panels
Organic solar panels, also known as plastic solar panels, use organic materials such as polymers and dyes to convert sunlight into electricity. They are generally cheaper to produce than traditional solar panels, but they are also less efficient and have a shorter lifespan. Organic solar panels are still in the experimental stage and are not yet widely available.
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
Building-integrated photovoltaics, or BIPV, are solar panels that are integrated into the design of a building, such as in the roof, walls, or windows. BIPV systems can help to reduce the overall energy consumption of a building, and they can also add to its aesthetic appeal. BIPV systems can be made using a variety of solar panel technologies, including monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin film.
Transparent Solar Panels
Transparent solar panels are a type of solar panel that allows visible light to pass through while still generating electricity. They are designed to be used in windows, skylights, and other areas where transparency is desirable. Transparent solar panels are still in the experimental stage and are not yet widely available.
While these other types of solar panels are not as common as the four main types, they show promise for future development and innovation in the solar industry.
FAQs
Do I Need to Install Batteries With My Solar Panel System?
While it is not required to install batteries with a solar panel system, doing so can help to store excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Different Types of Solar Panels for Heating Systems?
When considering solar heating system benefits, it’s important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of different types of solar panels. While monocrystalline panels offer high efficiency and longevity, they can be more expensive. Polycrystalline panels, on the other hand, are more affordable but slightly less efficient.
Do Solar Panels Require a Lot of Maintenance?
Solar panels require very little maintenance, as they have no moving parts and are designed to be durable and long-lasting. However, they may need occasional cleaning to remove dust and debris that can accumulate on the surface of the panel.
How Much Do Solar Panels Cost?
The cost of solar panels varies depending on several factors, such as the type of panel, the size of the system, and the location of the installation. On average, a residential solar panel system can cost between $15,000 and $25,000 before tax incentives and rebates.
Last Assumption
There are several types of solar panels available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Monocrystalline, polycrystalline, thin-film, bifacial, and other types of solar panels can all be used to generate clean, renewable energy from the sun.
Choosing a solar panel system, it’s important to consider factors such as efficiency, cost, and maintenance requirements, as well as the specific needs and limitations of your location and property. By harnessing the power of solar energy, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and help to create a more sustainable future for ourselves and the planet.
