The law of energy conservation states that when one form of energy is converted into another, the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant. If you take a certain amount of energy out of the system, an equal amount must be put back in. For example, if you use a machine to convert chemical energy into kinetic energy, the machine will eventually run out of fuel and stop working.
The law of energy conservation is one of physics’s most important laws. It states that when one form of energy is converted into another, the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant. This means that if you take a piece of coal and burn it to generate electricity, the total amount of energy in the universe does not change.
The same is true for any other type of energy conversion. This law is a fundamental principle of thermodynamics and has far-reaching implications for our understanding of the universe.
What Does the Law of Conservation of Energy State?

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. This law is a fundamental principle of physics. It was first postulated in the early 19th century by French physicist Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier and British chemist Humphry Davy.
The total energy of a system can be classified into two types: kinetic energy, which is the energy associated with motion, and potential energy, which is stored energy due to an object’s position relative to other objects or due to its condition (e.g., electrical charge). The energy conservation law states that the total amount of these two types of energies remains constant in an isolated system. A simple way to understand this concept is to consider a closed box filled with various objects.
If we were to measure the combined kinetic and potential energies of all the objects inside the box initially, then again at some later time, we would find that these energies remain equal. This would be true even if the objects inside the box move around or change their positions relative to each other—the total amount of kinetic and potential energies stays constant. The only way that the total amount of energy could change in this scenario is if some type of energy was added to or removed from the system (i.e., if there was an external force acting on the system).
It should be noted that the energy conservation law only applies to isolated systems—systems that do not interact with their surroundings. A more realistic example than our closed box scenario would be a planet orbiting a star. Since both bodies exert gravitational forces on each other, they are not considered to be isolated from each other. In general, anytime there are forces acting between two bodies, they are not considered isolated from each other, and therefore, the law does not apply.
Which Statement is Correct About the Law of Conservation of Energy?
In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. This law is a fundamental principle of physics and applies to any closed system. A system’s total energy can take many forms, including kinetic, thermal, electromagnetic radiation, and potential energy.
What Does the Law of Conservation?
In the physical sciences, the law of conservation states that certain properties of an isolated system remain constant over time. This principle was first articulated by French physicist Antoine Lavoisier in the 18th century and has since been applied to many different areas of study. The law is fundamental in thermodynamics, chemistry, and physics.
Energy Can’t be Created
The law of conservation states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be converted from one form to another. For example, when a car burns gasoline, the chemical energy in the fuel is converted into heat and motion. The total amount of energy remains the same, but its form changes.
Matters can’t be created.
This principle also applies to matter: Matter cannot be created or destroyed but can be transformed from one state to another. For example, water can exist as a liquid, solid (ice), or gas (vapor). The total amount of matter remains the same in any given reaction or process; it is only its form that changes.
Note
The law of conservation is a basic tenet of many scientific theories and laws, including the laws of thermodynamics and Newton’s laws of motion. It is also a key concept in engineering and technology, as it helps engineers design efficient systems and use resources effectively.
What are the 3 Laws of Conservation of Energy?
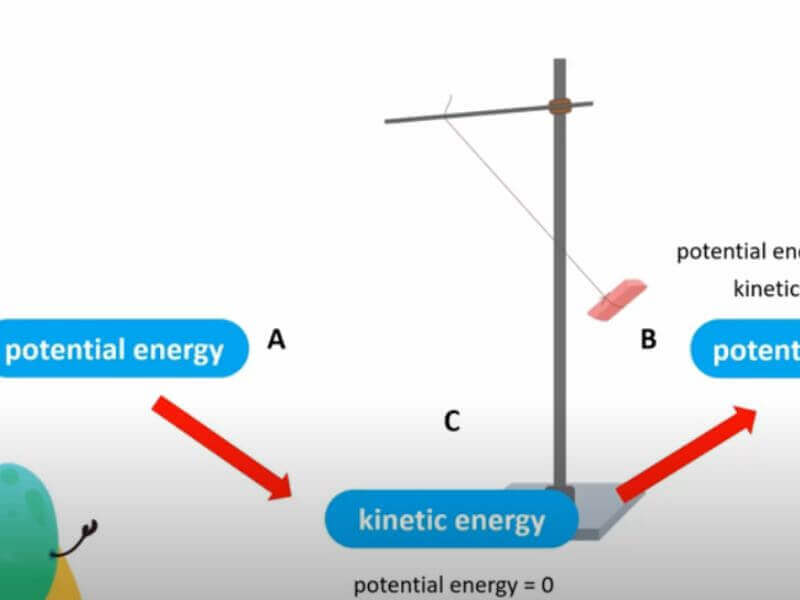
In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. This law is a direct consequence of the fact that matter and energy can neither be created nor destroyed; they can only be transformed from one state to another. The total amount of energy in the universe is thus always constant.
| First law | The first law of thermodynamics is also known as the law of energy conservation. It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In other words, the amount of energy in the universe remains constant, even though it may change its form (e.g., from chemical to heat). |
| Second law | The second law of thermodynamics says that when two systems are in contact, there will always be some energy transfer between them so that their energies become more equalized over time. In other words, entropy (a measure of disorder) always increases over time in an isolated system. |
| Third law | The third law of thermodynamics says that as a system approaches absolute zero (the lowest possible temperature), its entropy also approaches zero. |
Entropy is a measure of disorder, so all matter would be perfectly ordered at absolute zero and have no thermal motion.
The Law of Conservation of Mass States That
.In simple terms, the law of conservation of mass states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed. This means that the total amount of matter in the universe remains constant, even as it changes form.
The law is one of the most important principles in chemistry and physics and has many applications. Antoine Lavoisier first proposed the law of conservation of mass in 1789. Many people believed that matter could spontaneously appear or disappear at the time.
Lavoisier’s experiments showed that this wasn’t the case, and he developed a set of laws that govern how matter behaves. The law of conservation of mass is just one part of these laws, known as the laws of thermodynamics. Today, the law of conservation of mass is considered to be one of the most fundamental principles in all of science.
It’s used in a wide variety of fields, from engineering to biology. In each case, understanding how matter behaves is essential for making accurate predictions and designing effective experiments.
The Law of Conservation of Energy States That Energy Cannot Be Created Or Destroyed
The law of energy conservation is one of physics’s most important laws. It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be converted from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in the universe is always constant.
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental law of physics that has many applications in our everyday lives. For example, when you ride a bicycle, your legs push against the pedals to make the wheels turn. The pedals transfer this mechanical energy into kinetic energy, which makes the bike move forward.
But Where Does the Kinetic Energy Come from?
The answer is that it comes from the chemical energy stored in your food. When you eat food, your body breaks down the molecules and uses the chemical Energy to power your muscles.
So, ultimately, all of the Energy in your body comes from the sun. Plants use sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose and other sugars during photosynthesis. Animals then use these sugars as food.
Thus, every bit of Energy in your body can be traced back to sunlight! The conservation of energy law also has important implications for understanding how climate change works. The Earth’s climate is determined by the balance between incoming solar radiation from the sun (which warms our planet) and outgoing infrared radiation (which cools our planet).
If more energy was going out than coming in, our planet would gradually cool down; if more energy was coming in than going out, our planet would gradually heat up over time.
State the Law of Conservation of Energy With Example
The law of conservation of energy is one of the most important laws in physics. It states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can be converted from one form to another. The law is a consequence of the fact that the total amount of energy in the universe is constant.
The law of conservation of energy is often used to analyze physical systems. For example, when a ball is thrown into the air, its kinetic energy (energy of motion) decreases as it slows down. At the same time, its potential energy (energy due to its position) increases as it gets higher off the ground.
The sum of these two energies remains constant; this is an example of the law of energy conservation at work.
The Law of Conservation of Energy States That Brainly
The law of energy conservation is one of physics’s most important laws. It states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed. This means that the total amount of energy in the universe is always constant.
Energy conservation law is also known as the first law of thermodynamics.
What Does the Law of Conservation of Matter State?
The conservation of matter is one of the most important laws in chemistry. It states that matter can neither be created nor destroyed. This means that the amount of matter in a closed system will always remain the same.
This law has many applications in chemistry and is used to explain why you can’t create gold from other elements or how atoms are rearranged during chemical reactions, but the total number of atoms doesn’t change. Without the law of conservation of matter, our understanding of Chemistry would be very different. So next time you’re doing a chemistry experiment, remember that you’re following one of the most important laws in all science!
What Does the Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy State?
The law of conservation of mechanical energy states that the total mechanical energy in a closed system remains constant. This means that the sum of the kinetic and potential energy in a system will remain constant over time as long as no external forces are acting on the system. The law is a direct consequence of the fact that Newton’s laws of motion are time-reversible.
The law of conservation of mechanical energy can be used to solve problems involving objects in equilibrium, such as finding the height of an object from which it will fall without any external forces acting on it. It can also be used to find the speed at which an object will move when it reaches a certain point in its trajectory. In general, the law of conservation of mechanical energy is a useful tool for understanding and predicting the behavior of systems where no external forces are acting on them.
Who Discovered the Law of Conservation of Energy
The law of energy conservation is one of physics’s most important laws. It was first discovered by German physicist Hermann von Helmholtz in 1847. The law states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can be converted from one form to another.
For example, when a ball is dropped, the potential energy is converted into kinetic energy (the energy of motion). The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental law of physics that has many applications in our everyday lives. For example, it explains why a battery will eventually run out of power and why we need to eat food to maintain our body’s energy levels.
It also has important implications for the field of thermodynamics, which deals with the conversion of heat into other forms of energy.
The Law of Conservation of Energy | Forms of Energy
Final Note
The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental law of physics that states that when one form of energy is converted into another, the total amount of energy in the universe remains constant. This means that if you take a certain amount of energy out of the system, an equal amount must be put back in.
