A battery is a device that provides power to a circuit. It consists of one or more cells that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. The role of the battery is to provide the initial force that starts the flow of electrons around the circuit.
The battery supplies the energy to overcome any resistance in the circuit and to keep the current flowing.
A battery plays an essential role in making a complete circuit as it provides the necessary power to make the circuit work. Without a battery, a circuit cannot function properly. batteries come in many different sizes and shapes, and each type of battery has its own specific voltage and capacity.
The size and type of battery you need will depend on the application for which you are using the circuit.
What is the Function of a Battery in a Circuit?
A battery is a device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It is composed of one or more electrochemical cells. Each cell has two terminals, one positive and one negative.
When the cell is connected to an external circuit, it produces a voltage difference between its terminals. If the positive terminal of the cell is connected to the negative terminal of another cell, they form a series circuit called a battery pack.
Batteries are often used in electronic devices such as phones, laptops, and cameras.
The function of the battery in these devices is to provide power to the circuitry when there is no other source of power available, such as when the device is turned off or when it is not plugged into an outlet. In some cases, batteries may also be used to provide power to the device when there is an interruption in the main power supply, such as during a power outage.
What is a Battery in a Circuit?
In a circuit, the battery is the power source that provides the energy to make the current flow. The battery is like a pump that pushes electrons around the circuit. It has two terminals, positive and negative, which are connected to the wires in the circuit.
The battery creates a voltage difference between its terminals, which causes electrons to flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
What is the Function of a Battery?
A battery is an electrical device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It consists of one or more electrochemical cells, each of which contains a positive and a negative electrode separated by an electrolyte. When the electrodes are connected to an external circuit, electrons flow from the negative to the positive electrode, producing an electric current.
The function of a battery is to provide power to devices that use electricity, such as cell phones and laptops. Batteries store energy in their electrochemical cells until it is needed by the device. When the device is turned on, the battery provides the electrical energy necessary to operate it.
The Function of the Battery in a Circuit Class 10
A battery is a device that stores electrical energy and converts it into direct current (DC) electricity. It is made up of one or more electrochemical cells. Each cell has two electrodes, a negative electrode called the anode and a positive electrode called the cathode.
The anode is made of metal that can be oxidized, such as lead or zinc. The cathode is made of metal that can be reduced, such as copper or silver. A thin sheet of material called a separator separates the two electrodes to prevent them from coming into contact with each other.
When the circuit is closed, electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte and separator. This creates a potential difference between the two electrodes. The anode becomes negatively charged and the cathode becomes positively charged.
As long as there is a potential difference across the electrodes, electrons will flow through the circuit and power any devices connected to it.
5 Functions of a Battery
There are many types of batteries, but all batteries have five basic functions: to store energy, to release energy, to create a voltage potential, to reverse the flow of current, and to act as a resistor.
Store Energy
Batteries store energy in the form of chemical reactions. The most common type of battery is the lead-acid battery, which stores energy in the form of lead and sulfuric acid.
Releases Energy
When this reaction is reversed, it releases energy in the form of electrons. This flow of electrons creates a voltage potential across the battery’s terminals.
To Create a Voltage Potential
The voltage potential created by a battery can be used to power electrical devices. When electrons flow through an electrical device, they create a current. The amount of current that flows through a device depends on the resistance of the device and the voltage potential of the battery. Batteries can also be used to reverse the flow of current.
To Reverse the Flow of the Current
This is known as recharging. Recharging occurs when electrons flow from a higher voltage potential back into the battery’s chemical reaction. This reverses the storage process and allows batteries to be reused over time.
To Act as a Resistor
Finally, batteries act as resistors. Resistors are materials that resist or oppose the flow of electrons. In order for electricity to flow through a circuit, there must be some resistance in order to create an impedance mismatch.
Batteries provide this resistance by opposing electron flow with their own internal resistance.
What is the Source of Electricity in a Simple Electric Circuit?
Most electric circuits contain three basic elements: a power source, a conductor, and a load. The power source provides the energy that flows through the circuit. The conductor is a material that allows electrons to flow freely through it, making it an excellent choice for carrying electrical current.
The load is any device that uses electricity, such as a light bulb or motor. In a simple electric circuit, the power source is usually a battery. The conductor is typically a metal wire, and the load is often a light bulb or Resistor.
When the circuit is complete and all of the components are connected properly, electrons will flow from the negative terminal of the battery through the wire to the light bulb or Resistor. This flow of electrons makes the light bulb glow or causes current to flow through the Resistor. The source of electricity in an electric circuit is essential for providing the energy necessary to make things work.
Without it, there would be no way to get electrons flowing and no way to power devices that use electricity. Batteries are common sources of electricity in simple circuits because they provide a steady flow of voltage that can be easily controlled with switches.
What is the positive terminal of a battery called? Click here for details.
How Does a Battery Work?
Batteries are devices that store energy and convert it into electricity. There are many different types of batteries, but all work on the same principle. A battery has two terminals, a positive (+) and a negative (-).
When the battery is connected to an electrical circuit, electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. This flow of electrons produces an electric current which can be used to power electrical devices. Batteries are made up of one or more cells.
Each cell contains chemical reactions that generate electrons. The number of cells in a battery determines its voltage. For example, a typical AA battery has 1.5 volts.
The first batteries were invented in the early 1800s by Italian physicist Alessandro Volta. His invention was called the voltaic pile and consisted of stacks of alternating zinc and copper discs separated by moistened cardboard disks soaked in brine (salt water). When connected together in a circuit, these discs produced enough electricity to power small devices such as telegraphs.
A Component of a Circuit That is Commonly Represented by a Cell Or a Battery
When you think about a circuit, you might picture a tangled mass of wires. But circuits are actually quite simple: they’re just a path for electrons to flow. And in order to create that path, you need three things: conductors (things that allow electrons to flow freely), insulators (things that don’t allow electrons to flow), and a power source.
The power source is the most important part of the circuit because it provides the energy that makes the whole system work. Without it, there would be no flow of electrons and therefore no circuit. The power source is commonly represented by a cell or battery.
A cell is an electrochemical device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It consists of two electrodes (a positive and a negative) immersed in an electrolyte (a conducting solution). When the cell is connected to an external load, such as a light bulb, the chemical reaction between the electrodes and electrolyte produces an electric current flowing through the load.
Batteries are made up of one or more cells connected together. They provide higher voltages than single cells, making them ideal for powering devices like flashlights and computers. Batteries also last longer than cells because they can store more energy.
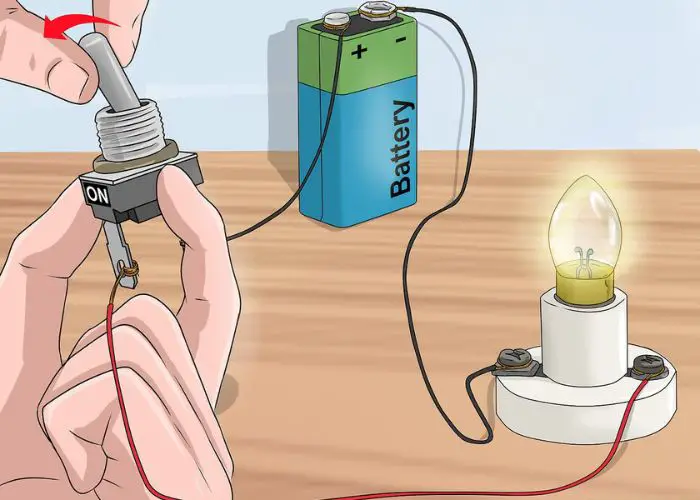
What is the Role of the Battery in a Circuit?
Batteries are devices that store energy and release it as electricity. They are an essential part of many electronic circuits. Without a battery, circuit components like LEDs would not be able to light up.
Batteries work by using two different metals that react chemically with each other to create an electric current. The two metals are called electrodes, and the material between them is called an electrolyte. When the electrodes are connected to a circuit, the electric current flows through the circuit and powers the devices in it.
The strength of the electric current produced by a battery depends on its type and size. The most common type of battery used in electronics is the AA battery. AA batteries come in different sizes, but they all produce 1.5 volts of electricity.
How Does a Battery Complete a Circuit?
A battery is a device that stores chemical energy and makes it available in an electrical form. When a battery is connected to a circuit, electrons flow from the negative terminal through the circuit to the positive terminal. This flow of electrons provides power to run electric devices.
Batteries have two terminals, positive (+) and negative (-). The negatively charged electrons want to flow to the positive side, but they can’t because there’s nothing for them to flow through. So, we put a material between the electrodes that provide a path for them to flow.
This material is called an electrolyte. When you connect a battery to a circuit, you’re creating a closed loop: The electrons travel from the negative terminal through the wires and devices in your circuit and back into the positive terminal of the battery. As long as there’s no break in this loop, the current will continue to flow and your devices will keep running.
What is the Purpose of the Batteries?
Batteries are devices that store chemical energy and convert it to electrical energy. The most common type of battery is the lead-acid battery, which is used in cars and trucks. Other types of batteries include lithium-ion batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries, and nickel-metal hydride batteries.
The purpose of a battery is to store energy so that it can be converted into electricity. Batteries are used in many devices, including cell phones, laptops, and power tools.
Last Point
In order for an electric circuit to be complete, it needs three things: a power source, a conductor, and a load. The power source provides the electrons that flow through the circuit. The conductor provides a path for those electrons to follow.
And the load uses the electrons to do work. But there’s one more important piece of the puzzle: the battery. Batteries provide a potential difference, or voltage, which is necessary for the circuit to work.
Without batteries, circuits wouldn’t be able to do anything useful.
Read More:
- Can LED Lights Cause Battery Drain?
- Can You Charge a 24V Battery With a 20V Charger?
- Do You Need to Charge Car Key?
- What Happens If I Hook My Battery Up Backwards?
Used Resources:
