A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a generator. Generators can be used to power homes and businesses, as well as provide backup power during an outage. There are many different types of generators, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.

A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a generator. Generators can be used to power homes and businesses, as well as provide backup power during an outage. There are many different types of generators available on the market, so it is important to choose the right one for your needs.
If you are looking for a generator to power your home or business, you will need to determine how much power you need. This will help you narrow down your options and choose the right size generator for your needs. You will also need to decide whether you want a portable or standby generator.
Portable generators are great for camping trips or tailgating, while standby generators are permanently installed and wired into your home’s electrical system. Once you have determined what type of generator you need, you can start shopping around for the best deal. Be sure to compare prices and features before making your final purchase decision.
What is a Device That Converts Mechanical Energy into Electrical Energy?
A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a generator. Generators come in many different sizes and shapes, but all work by using a rotating coil of wire to create an electromagnetic field. This field can then be used to power electric devices or to charge batteries.
How Does a Device That Converts Mechanical Energy into Electrical Energy Work?
The principle of operation for an electrical generator is based on the relationship between magnetism and electricity. An electric current generates a magnetic field, while a moving magnetic field induces an electric current. This interaction can be used to generate electricity from mechanical energy, as in the case of a turbine-driven generator.
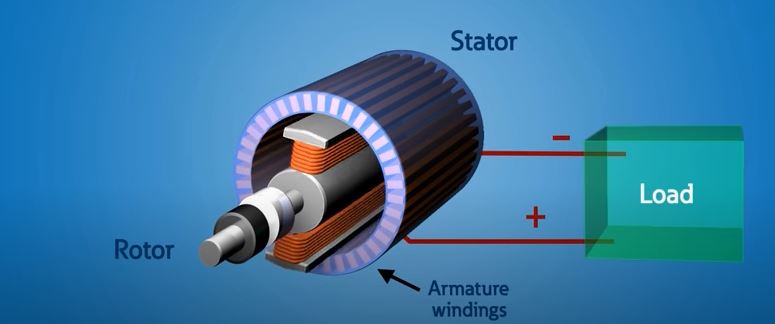
A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy typically contains three main components: a rotor (the part that rotates), a stator (the stationary part), and magnets. The rotor is attached to the shaft of a prime mover such as a turbine, water wheel, or reciprocating engine. As the rotor turns, it spins the magnets inside the stator.
The spinning magnets produce an electromagnetic field that interacts with the winding coils in the stator to induce an electric current. The current is then sent to an external load (such as your home’s electrical panel) through slip rings and brushes.
What are the Benefits of Using a Device That Converts Mechanical Energy into Electrical Energy?
An electrical device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a generator. Generators are used in a variety of applications, including providing backup power for homes and businesses during an outage, powering construction equipment on job sites, and delivering electricity to remote locations where the grid does not reach. There are many benefits of using a generator, including:
Reliability
When the power goes out, generators can keep your lights on and your appliances running. This can be especially important for businesses that cannot afford to lose power or go without heat or air conditioning for extended periods of time.
Convenience
Portable generators can be used to power RVs, campers, and other recreational vehicles when away from home. They can also be used to run essential devices during a blackout or natural disaster.
Affordability
Generators are available in a wide range of prices and sizes, so there is an option for every budget. Additionally, they typically last for many years with proper maintenance, making them a wise investment.
An Electrical Generator is a Device That Converts Electrical Energy into Mechanical Energy
An electrical generator is a device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The most common type of electrical generator is the alternator, which converts alternating current (AC) into mechanical energy. Other types of generators include direct current (DC) generators and hydroelectric generators.
The basic principle behind all electrical generators is the same: they use a conductor to create a magnetic field, which in turn creates an electric current. The conductor is usually a coil of wire, called the armature, that is rotated inside a larger coil of wire, called the stator. As the armature rotates, it cuts through the magnetic field of the stator, inducing an electric current in the armature.
This current is then used to power an electric motor or other loads. The efficiency of an electrical generator depends on several factors, including its design, the materials used to construct it, and how well it is maintained. Generators can be very efficient; however, some designs are more efficient than others.
For example, brushless alternators are typically more efficient than their brushed counterparts because they have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance.
Converting Mechanical Energy into Electrical Energy Examples
There are many ways to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. One example is using a hydraulic turbine. When water flows through a turbine, the blades spin and this, in turn, rotates a generator.
The generator then produces electricity. Another example is using an internal combustion engine. When gasoline or diesel is burned in an engine, it turns the crankshaft.
The crankshaft is connected to a generator and as it turns, it produces electricity.
Name the Device That Converts Chemical Energy into Electrical Energy
The device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy is called a fuel cell. Fuel cells are devices that create electricity by converting the chemical energy of a fuel into electrical energy. The most common type of fuel cell uses hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, but there are also other types of fuel cells that use other fuels such as natural gas, methanol, or coal.
What Type of Energy Do Generators Turn into Electricity?
Most generators are used to create electricity using a rotating magnetic field to turn mechanical energy into electrical energy. There are several types of devices that can be used to create this rotating magnetic field, including steam turbines, water wheels, and internal combustion engines.
Which of the Following Situations Illustrate How a Simple Electric Motor Works?
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The most common type of electric motor is the brushed DC motor, which consists of a rotating armature (or rotor) with permanent magnets on the outside and brushes on the inside. When electricity flows through the brushes, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the field of the magnets to make the armature rotate.
There are many different types of electric motors, but they all work on the same basic principle: using electromagnetism to create a force that turns an object. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at how electric motors work and how they’re used in everything from cars to hair dryers.
Temporary Magnet Caused by Moving Electric Current Through a Conductor.
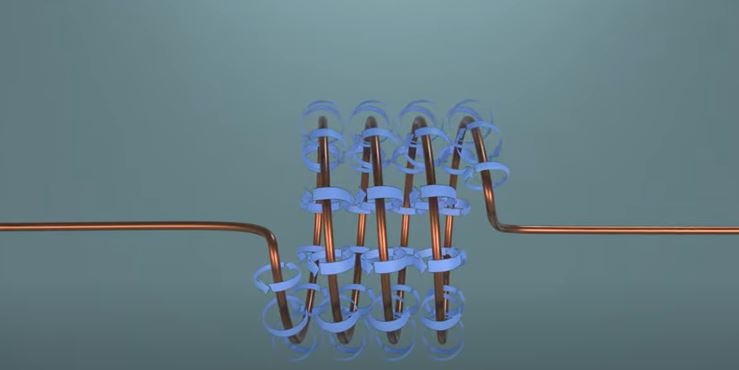
A moving electric current can create a temporary magnet. This is because the moving electrons create a magnetic field. The strength of this magnetic field depends on the amount of current flowing through the conductor.
Devices That Convert Energy from One Form to Another
In our homes, we use devices that convert energy from one form to another all the time. For example, when we turn on a light, electrical energy is converted into light and heat. When we cook food in a microwave oven, electrical energy is converted into heat.
We also use devices that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. For example, when we ride a bike, our pedaling turns gears that spin a magnet inside of a coil of wire. This generates electricity that can be used to power lights or other devices on the bike.
There are many different types of devices that convert energy from one form to another. Here are just a few:
| 1 | Solar panels | Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. |
| 2 | Wind turbines | Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of moving air into electricity. |
| 3 | Hydroelectric dams | Hydroelectric dams convert the potential energy of stored water into electricity. |
| 4 | Fuel cells | Fuel cells convert chemical energy into electricity. |
What Type of Material Does Not Allow Electrons to Flow Easily?
There are many materials that do not allow electrons to flow easily. These include:
- Metals such as aluminum and copper;
- Semiconductors such as silicon and germanium;
- Insulators such as glass and rubber;
These materials have different properties that make them difficult for electrons to flow through them.
For example, metals have a large number of free electrons that can move around easily. This makes it difficult for an electric current to flow through them. Semiconductors have a smaller number of free electrons, but they are still too high to allow easy electron flow.
Insulators have very few free electrons and this makes it impossible for electric current to flow through them.
Conclusion
This blog post discusses the different types of devices that can convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The most common type of device is a generator, which uses magnets to create an electric current. Other devices include wind turbines and hydroelectric dams, which use the kinetic energy of moving water or air to generate electricity.
Used Resources:
