Most people think that a battery is a conductor of electricity, but this is not the case. The battery does not conduct electricity, rather it produces an electric current. The electric current produced by a battery is caused by the flow of electrons from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
This flow of electrons is what allows for the transfer of electrical energy from one point to another.
Yes, a battery is a conductor of electricity. When the two ends of a battery are connected together with a conducting material (such as a wire), an electric current will flow through the circuit, and the charge will flow from one end of the battery to the other. This is because batteries have a built-in electric potential difference that drives electrons through the circuit.
Is a Battery an Insulator?
No, a battery is not an insulator. An insulator is a material that does not allow electricity to flow through it easily. This is why things like rubber and glass are used to insulate electrical wires.
A battery, on the other hand, is made of materials that allow electricity to flow freely through them. The purpose of a battery is to store energy in the form of electric charge.
How Do Batteries Produce Electricity?
Batteries produce electricity by a process called electrolysis. This is when electrons are forced to flow through a conducting medium, such as a metal wire, by an electric potential difference. The potential difference forces the electrons to flow from one atom to another, resulting in the creation of an electrical current.
What is a Battery in a Circuit?
Batteries are one of the most important components in any circuit. They provide the power necessary to run the circuit and allow it to function properly. Without a battery, a circuit would not be able to operate.
A battery is essentially a container that stores electrical energy and makes it available on demand. The first batteries were created in the 1800s and they have been an essential part of electronic devices ever since. Today, there are many different types of batteries available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common type of battery used in circuits is the lead-acid battery. Lead-acid batteries are inexpensive and have a long shelf life, but they are also heavy and can leak acid if damaged. Lithium-ion batteries are another popular choice for circuits; they are lighter than lead-acid batteries and don’t leak, but they can be more expensive.
No matter what type of battery you use in your circuit, it’s important to make sure that it is sized correctly for the load being placed on it. If too much current is drawn from the battery, it can overheat and cause damage to both itself and the surrounding circuitry. Likewise, if a battery is too small for the load being placed on it, it will be unable to provide enough power and the circuit may not function properly.
Is a Light Bulb a Conductor Or an Insulator?
A light bulb is an incandescent lamp that produces light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is usually made of tungsten because it has a high melting point and resistance to evaporation. A typical household light bulb uses about 60 watts of power and lasts for about 1,000 hours.
If you’re looking for the best motorcycle USB charger on the market, look no further! Our charger is designed to charge your devices quickly and efficiently, so you can enjoy your ride without worrying about your battery life. Read the article for details.
Is a Switch a Conductor Or an Insulator?
Is a Switch a Conductor or an Insulator? This is a question that often comes up when discussing electrical circuits. The answer, like many things in life, is “it depends.”
In general, switches are made from either conductive or insulating materials. However, the type of switch will dictate whether it acts as a conductor or an insulator. Here’s a quick rundown on the different types of switches and how they work:
SPST (Single Pole Single Throw) switches are the most basic type of switch. They are typically used to turn a circuit on or off. SPST switches are usually made from a conductive material, which makes them good conductors.
However, there are some SPST switches that are made from insulating material. These types of switches are used in applications where high voltage is present. DPST (Double Pole Single Throw) switches are similar to SPST switches, but they have two sets of contacts instead of just one.
This allows them to control two circuits at once. DPSTswitch es can be made from either conductive or insulating material. If the switch is made from a conductive material, then it will act as a conductor.
If the switch is made from an insulating material, then it will act as an insulator. It all depends on the application for which the DPST switch is being used.
How are Batteries Made?
Batteries are made of three main parts: the anode, the cathode, and the electrolyte. The anode is made of carbon, while the cathode is usually made of metal oxide. The electrolyte is a solution that allows electrons to flow between the anode and cathode.
When a battery is charging, electrons flow from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte. This creates a potential difference between the two electrodes, which allows electric current to flow when the battery is discharged.
How Does a Battery Work?
How Does a Battery Work? Batteries come in all shapes and sizes, but they all have one common goal: to store energy. Batteries are made up of one or more cells, each of which contains an electrolyte and two electrodes (a cathode and an anode).
The electrolyte is a substance that allows electrons to flow freely between the electrodes. When the battery is connected to an external circuit, the electrons flow from the negative electrode (cathode) through the electrolyte to the positive electrode (anode), creating a current. This current can be used to power devices such as flashlights or cell phones.
The amount of energy a battery can store depends on its size and chemical composition. The most common type of battery is the lead-acid battery, which is often used in cars. Lead-acid batteries work by converting chemical energy into electrical energy.
The chemical reaction that occurs inside the battery produces lead sulfate and water. These products build up on the electrodes over time, reducing their effectiveness and eventually causing the battery to fail.
What Does a Battery Do in a Circuit?
A battery is a device that stores energy and can be used to power a circuit. The battery provides a source of electrons that flow through the circuit to power the devices in the circuit.
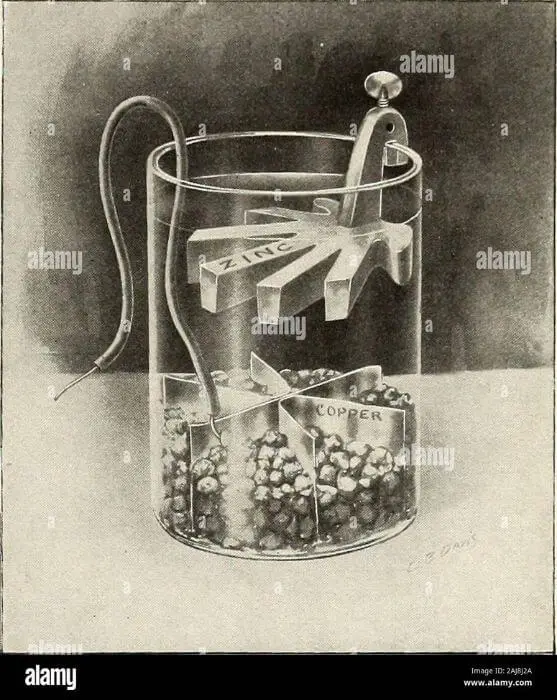
Does a Battery Conduct Electricity?
Yes, a battery does conduct electricity. This is because a battery contains two or more electrochemical cells that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. Each cell has two electrodes, one of which is positive and the other negative.
When the circuit is closed, electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode through an external load, such as a light bulb or motor. This flow of electrons produces an electric current.
Is Battery an Insulator Or Conductor?
This is a question that often comes up, and unfortunately, there is no simple answer. It depends on the type of battery, as well as the material it is made from. Generally speaking, batteries are insulators.
This is because they are designed to store energy in the form of electrical potential energy, and if they were good conductors, this energy would be dissipated too quickly. However, there are some types of batteries that are better conductors than others. These include lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries.
These types of batteries are able to store more energy than traditional insulating batteries, making them ideal for applications where high power output is required (such as in electric vehicles).
What Type of Electricity is a Battery?
A battery is a type of electricity that is created by the chemical reaction between two different metals. The most common types of batteries are lead-acid batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries, and lithium-ion batteries.
What Makes Batteries Electrically Conductive?
Batteries are electrically conductive because they contain a chemical reaction that produces electrons. This reaction is between the anode and cathode of the battery, with the anode being the negative electrode and the cathode being the positive electrode. The electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through an electrolyte, which is a liquid or gel that contains ions.
When the battery is connected to an external circuit, these electrons can flow through the circuit and power a device.
In a Nutshell
Yes, a battery is a conductor of electricity. It is made up of two electrodes, the anode, and the cathode, which is separated by an electrolyte. The anode is negatively charged and the cathode is positively charged.
When the battery is connected to a circuit, the electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte.
